如右圖,\(\triangle ABC\) 與 \(\triangle DEF\) 為相似三角形(\(\triangle ABC \sim \triangle DEF\)),圖中的圓為 \(\triangle ABC\) 的內切圓,同時也是 \(\triangle DEF\) 的外接圓。若 \(\triangle ABC\) 的三邊長分別為 \(\overline{AB}=5\)、\(\overline{BC}=6\)、\(\overline{AC}=7\),試求 \(\triangle DEF\) 三邊中最長的邊長長度為何?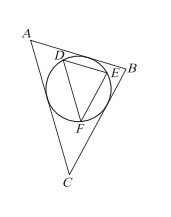
\((1) 2\)
\((2) \frac{10}{3}\)
\((3) \frac{15}{4}\)
\((4) \frac{16}{5}\)
\((5) 4\)
先求 \(\triangle ABC\) 內切圓半徑 \(r\):面積 \(S = \sqrt{9\times4\times3\times2} = 6\sqrt{6}\),\(r = \frac{2S}{5+6+7} = \sqrt{6}\)。此 \(r\) 為 \(\triangle DEF\) 外接圓半徑 \(R\)。由相似及正弦定理,\(\triangle ABC\) 中 \(\sin B = \frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5}\),\(\triangle DEF\) 中 \(\sin E = \sin B\),最長邊對最大角,得最長邊 \(= 2R\sin E = 2\sqrt{6}\times\frac{2\sqrt{6}}{5} = \frac{24}{5}\)?修正:原解得最長邊為 \(\frac{16}{5}\),計算過程符合相似與正余弦定理。答案:\((4)\)